What is a Laser printer?
A laser printer is a popular type of personal computer printer that uses a non-impact
photocopier technology.
When a document is sent to the printer, a laser beam "draws" the document on
a selenium-coated drum using electrical charges. After the drum is charged, it is rolled in toner,
a dry powder type of ink. The toner adheres to the charged image on the drum.
The toner is transferred onto a piece of paper and fused to the paper with heat and pressure.
After the document is printed, the electrical charge is removed from the drum and the excess
toner is collected. Most laser printers print only in monochrome.
A color laser printer is up to 10 times more expensive than a monochrome laser printer.
IBM introduced the first laser printer in 1975 for use with its mainframe computers. In 1984,
Hewlett-Packard revolutionized laser-printing technology with its first LaserJet,
a compact, fast, and reliable printer that personal computer users could afford.
Since then, laser printers have decreased further in price and increased in quality.
Hewlett Packard continues to be the leading manufacturer with competitors including Lexmark,
Okidata, and Xerox.
Here are the some features of Laser printer:
- Resolution
Laser printer imaging paper can have various resolutions ranging from
300 laser dots per inch (dpi) to up to 1200 dpi.
The laser produces smaller and smaller dots for corresponding increases
in the number of dots per inch. Laser printer imaging paper rarely has
resolutions exceeding 1200 dpi because the physical properties of the toner
cannot be reduced to smaller particles.
As the resolution increases, so does the smoothness and clarity
of the printed image. Smaller and smaller dots arranged in curves and
gradients result in less jagged edges and more subtle changes in screens.
The higher the resolution, the more shades of gray are available.
Three hundred dpi laser printers can produce 16 shades of gray, while 1200 dpi
printers can produce 128.
- Speed
Laser-printer speed is rarely restricted by
the mechanical ability to move the paper.
Speed is determined by the laser's ability to image the drum for repeated
passes. Also, laser-printer speeds are affected by the computing power available
to process and translate the image for the laser. Laser printers have processors
and random-access memory (RAM), just like the computer used to produce the
original file. Some laser printers have hard drives for storing data such as font
files and other necessary graphic files. All of these factors can affect the laser
printer's speed, measured in pages per minute. A relatively slow laser printer may
run at 12 to 16 pages per minute. Faster laser printers can reach speeds of over
60 pages per minute. These machines are used for high-end graphic production
such as address mailers and advertising supplements.
- Color
Color laser printers work identically to black-only laser printers with
one exception. Instead of one drum and one toner,
the printer has four: black, cyan (a light blue), magenta (a pinkish red) and yellow.
The four lasers image four drums, and the sheet of paper passes each drum
separately. Once all four toners are on the paper, it is fused.
Color laser printers usually come in only 1200 dpi resolutions in order to produce
accurate color. Also, color laser printers run at relatively lower speeds because
of the complexity of aligning the paper for accurate color registration and multiple
laser and toner operations.
- Paper Handling
Referring to the size and type of paper the printer
can handle and in what quantity, paper handling is an
important laser printer feature. Most laser printers use standard-cut paper
stock. While the vast majority of printers can handle standard business
stationery, such as A4 paper, A5 paper, and envelopes, most paper trays are only
suitable for A4 paper stock. The printers generally have a manual feed option to
allow for different paper, envelopes, or even card to feed through.
To print on sizes larger than A4, such as A3 paper, you need a laser printer larger
than your average desktop model, with a small footprint.
What is Inkjet printer?
An inkjet printer is a computer peripheral that produces hard copy
by spraying ink onto paper. A typical inkjet printer can produce copy with a resolution of at least
300 dots per inch ( dpi ). Some inkjet printers can make full color hard copies at 600 dpi or
more. Many models include other devices such as a scanner , photocopier , and dedicated fax
machine along with the printer in a single box.
In the inkjet printing mechanism, the print head has several tiny nozzles, also called jets.
As the paper moves past the print head, the nozzles spray ink onto it, forming the characters
and images. An inkjet printer can produce from 100 to several hundred pages, depending on the
nature of the hard copy, before the ink cartridges must be replaced.
There is usually one black ink cartridge and one so-called color cartridge containing ink in
primary pigments (cyan, magenta, and yellow). Some inkjet printers use a single cartridge with
cyan, magenta, yellow, and black ink. A few models require separate cartridges for each primary
pigment, along with a black ink cartridge.
The principal advantage of inkjet printers is the fact that most of them are inexpensive.
Inkjet printers are often given away at computer superstores along with the purchase of a
personal computer or substantial peripheral. Even the cheapest inkjet printers are satisfactory
for most of the needs of personal computer users. High-end inkjet printers can render digital
images on special paper, with quality rivaling that of professionally produced glossy or matte
photographs. Another advantage of inkjet printers is their light weight and modest desktop
footprint . Many models are easy to transport, and are preferred by traveling salespeople for
this reason alone.
Here are the some features of Inkjet printer:
- Inkjet printers use a small footprint and are easy to move around, which makes them reasonablyportable in a small business or home office environment.
- The average weight is around 20 pounds and most inkjet printers are plug-and-play devices, with ink
- cartridges easily snapping into place. Because of the ink technology where thousands of ink droplets are shot onto the paper, image quality can be outstanding, especially with color photos.
- There are photo-specific inkjet models available for this market that will reproduce photos with exceptional clarity and vivid colors.
- Inkjet printers are known to be cost-effective, with most of the models in this category being an All-in-One or Multi-Function device. This allows users to have a copy, print, scan and fax function in one easy-to-use printer thus eliminating the need for multiple machines.
Inkjet vs. Laser: A Quick Comparison
- Inkjets “see” the images they print as a series of tiny points, and lasers “see” these images as a geometric shape through mathematical values.
- Depending on the paper used, inkjet images have a possibility of appearing blurry due to absorption into the paper. Laser images do not have this risk, because the toner is fused with heat into the fibers of the paper.
- Inkjet printers are more economical to purchase, but the ink can be costly. Laser printers generally require a larger investment upfront, but the toner cartridges need replacing less often and have a more rapid print speed.
PRICE COMPARISON
- Inkjet printer price:
Canon Pixma MG2577s All-in-One InkJet Printer (Blue/White)
by Canon
2,499 RS.
HP DeskJet 2131 All-in-One Printer
by HP
2,799 RS.
Epson L380 All-in-One Ink Tank Printer
by Epson
10,229 RS.
- Laser printer price:
HP LaserJet Pro M126nw Multi-functional Printer
by HP
14,300 RS.
Ricoh SP210SU Monochrome Multi-Function Laser Printer
by Ricoh
8,499 RS.
Canon MF249DW All-in-One Laser Printer with Duplex,WiFi
by Canon
34,999 RS.
Managing our Print Environment Across Multiple Locations
If our organization has multiple locations and relies on print servers, the chances are good that our printing environment resembles one of two scenarios:
- A centralized print server at the main location that services all branch locations.
- Local print servers at each of the branch locations.
The first printing environment makes it a bit easier to manage printing because all print functionality is consolidated and routed through the central print server – which is generally close to where the primary IT management team is based. But it also introduces several vulnerabilities, chief among them being the WAN connection.
With a centralized print server, any print jobs initiated at remote branches have to first travel across the WAN to the central print server, then back across the WAN to the local printer. If this WAN link fails for any reason during that round trip, so does that print job. Even during day-to-day printing, the overtaxed WAN link can result in sluggish print jobs. The centralized server also introduces a single point of failure throughout the entire printing environment. When that print server goes down, the whole enterprise print environment does too. That can be addressed in part through redundancy, but redundancy is expensive and comes with its own management headaches.
In the second type of printing environment, the vulnerabilities are fewer, but it's no longer as easy to manage printing across the enterprise. In fact, it's downright difficult. That's because having discrete print servers at each location creates fragmentation. This in turn reduces the transparency of the company-wide printing environment and multiplies the burden on the technical and support staff. Instead of dealing with the maintenance and management of a single printing environment, they now have to deal with what are effectively several micro-environments, each with its own distinct needs.
To manage printing in any kind of distributed printing environment without the drawbacks of a centralized print server or multi-site servers, there's PrinterLogic. Our on-premise print management solution delivers unprecedented flexibility while giving you greater control over your whole printing environment.
for starters, PrinterLogic allows us to manage printing anywhere in our organization from a single pane of glass. Using web-based administration panel, we can easily deploy printers and drivers to end users in remote sites from a central console in the main location – manually or automatically, all without group policy objects (GPOs) or scripts. From this same console we can also alter printer settings, remove printers, and edit driver profiles. It doesn't matter if our headquarters is in Ahmedabad and the remote site is in USA. It's straightforward and consistent to manage printing with PrinterLogic.
PrinterLogic makes it easier on your support staff too. By providing an accessible self-service portal for end users, our next-gen print management solution allows them to easily identify and install nearby printers on their own. There's no need for them to call the service desk, because now printers can be installed with a single click in any printing environment. There's even an option to upload floorplan maps to make it easier for them to visually locate their desired printers. This feature is incredibly useful for roaming employees who travel between headquarters and remote sites.
There's no doubt that multiple locations present several hurdles when we are looking to manage printing across distributed printing environments. But Printer Logic's enterprise printing solution allows you to sail over those hurdles with incredible ease.
Features of multifunctional printer:
Convenience
A multifunction printer offers the convenience of additional features you may not have purchased otherwise. For example, if you normally do not send or receive many fax messages, you may not have invested in a separate fax machine. However, a multifunctional printer that includes fax capabilities allows you to send or receive the occasional fax without an added expense. In addition, the ability to scan an image and then print that image using the same machine offers another level of convenience by saving you the time of walking to two separate devices.
Space Savings
Perhaps one of the greatest advantages of a multifunctional printer includes the space savings offered by the device. Rather than having to find space for a printer, a copier, a fax machine and a scanner, you can have the same functionality in a single machine. This space savings may benefit those trying to make the most of their home office space or those working with significant space constraints.
Cost Savings
Another advantage of a multifunctional printer includes the cost savings of purchasing one device that performs multiple functions. Although the purchase price for an all-in-one printer may exceed that of a traditional printer, the overall cost typically remains less than purchasing multiple machines. Therefore, you can benefit from increased functionality without paying for each feature. In addition to the savings associated with the original purchase price, maintaining one device costs less than maintaining multiple devices.
Power Savings
Multifunction printers typically require one cord to power the entire device. Not only does this reduce cable congestion, it lowers the electricity required to run the device. This power savings also leads to increased cost savings.
₹ 9,699
features:
- Inkjet Printer
- Print, Copy, Scan
- Color Print
- USB Support
₹ 5,699
- Inkjet Printer
- Print, Copy, Scan, Fax
- Color Print
- USB & Wireless Support
Future of printing:
The Exciting Future of Printing
The earliest form of printing tool developed by humankind came in the form of cylinder seals made from stones, gems, glass, and ceramics. First produced in Susa in ancient Iran and the Sumerian city of Uruk in Mesopotamia more than 5,500 years ago, these small cylindrical objects bore engravings of written text and scenes depicting people and animals. The cylinders were rolled on pieces of clay tablets so that the engravings could be imprinted on them. These clay tablets, which often served important social or administrative functions, were among the first documents ever produced by our species.
Fast-forward to the 21st century, and one will find that this ancient tool has blossomed and branched out into a dazzling array of modern technologies that are defining people’s lives and shaping the world today. From environmentally sustainable printing techniques to 3D printing technologies that are democratizing manufacturing in ways never seen before, printing has definitely come a long way from its seal and clay beginnings.
As the years go by, however, printing technologies will continue to evolve. What does the future hold for the industry? Here are some exciting new developments and paradigm shifts that we can all look forward to.
The printing process will become more eco-friendly
People nowadays are becoming more aware of environmental issues and the negative impact of the culture of reckless consumption. As this trend continues, we will see market regulations tightening in many jurisdictions all over the world.
New legislations will favor more environmentally sustainable printing practices, including the recycling and remanufacturing of printer cartridges and paper products to divert the majority of unwanted paper, plastic, metal, and chemicals away from the waste stream. Current estimates show that some 400,000 tons of waste can be kept out of our landfills each year if only we remanufactured our printer cartridges instead of producing new ones.
Aside from recycling, the production of more sophisticated ink products that are gentler to the environment will also be undertaken in earnest by future generations. For instance, vegetable-oil based inks and ultraviolet-curable inks will be favored over traditional, solvent-based inks, which release more environmental pollutants. Additionally, food-safe inks will also be developed for the needs of the food and beverage industry.
3D printing will change our lives
The technology behind 3D printing may seem so wondrous to many people, but one can argue that it is really just the logical next step in the evolution of the ink-on-substrate printing technology. Now, thanks to a process known as additive manufacturing, we are not only able to print flat images on the surfaces of substrates, we can also print three-dimensional objects out of materials like plastic resin. The process involves the successive deposition of layers of this material until the object takes its final shape.
The future implications of this technology are enormous. As it becomes more affordable, more accessible, and more advanced, 3D printing can revolutionize manufacturing by allowing production to take place near or exactly at the point of consumption. Meaning to say, ordinary individuals will be able to manufacture the goods they need, when they want them. Current economic models will shift, as the manufacturing powerhouses that we know of today—whether countries or corporations—will no longer have the distinct advantages that they possess at present.
Another implication is that prototyping and customization in manufacturing will be so much easier. Creativity will be the name of the game, and with prototyping and customization becoming so effortless, innovators will be able to focus on the creating groundbreaking tools and contrivances that will address many of the problems that plague our lives today.
Advanced technologies will bring printing to new heights
Have you ever heard about photonic printing? How about conductive inks? If you haven’t yet, you soon will because advanced technologies such as these will introduce human civilization to the next age of printing.
Photonics, the science of light or photon generation, detection, and control, is currently being applied by innovative organizations that are hoping to develop invisible photonic printing techniques. The technology will be valuable for a variety of applications, including for identification and watermarking purposes, for anti-counterfeiting and anti-forgery endeavors, as well steganography, the practice of hiding messages or information within readable text or visible images.
Conductive inks, on the other hand, have the potential to change the way the printed medium is used for communication, marketing, and advertising. Currently being produced from materials like silver nanoparticles and conductive polymers, these inks are essentially circuits that allow the paper or substrate to become connected to the digital word. Imagine a seemingly ordinary poster having the same kind of capacitive sensing capability like a touchscreen display.
Conductive ink can be used in many other applications, including the production of smart clothing printed with flexible electronic inks, as well as the creation of soft machines, like bendable robots that can be used for search and rescue operations.
If someone ever tells you that printing has had its day and it’s doomed to oblivion in the near future, remember what you read here. Tell those folks that one day, people will actually be 3D printing their own homes and will be exchanging secret love notes printed with invisible photonic ink.
Google Cloud Print
Google Cloud Print is an online service that lets end users print to compatible printers, regardless of location.
Google cloud remote printing works by transmitting data from an endpoint device to a Google server and then to the selected printer, all over a secure Web connection.
The service is available through the Google Chrome browser, Google's mobile apps such as Gmail and Docs, and other supported iOS, Android, Windows and Mac apps. It is also the default printing method on Chromebooks.
Google Cloud Print is an under-appreciated service that can send print jobs from virtually anywhere to a connected printer in any other location. Normally that involves tedious configuration on your network, but Cloud Print can do it in just a few minutes. It's really easy to set up, and there are a few things you can do to extend its support beyond the browser to make all your printing tasks a lot easier. Here's a look at what it can do, how you can set it up, and how to make it even better.
What You Can Do With Google Cloud Print
Google Cloud Print makes it possible to send any document or image to a printer from any location. For example, if you wanted to print out a letter at home while at work, you could use the service to send that letter to your home printer and have it waiting for you when you get back. Normally this kind of setup requires a tedious network configuration, but with Google Cloud Print you just click a few buttons and you're done. The service can also print web pages and other documents to PDF format and save them in your Google Docs account. This is can be especially handy if you're keeping your account synchronized with all your computers using a third-party service called InSync (more info here). Basically, if you want to print anything from any device to practically any location, Google Cloud Print can make that happen.
If you want to get started with Google Cloud Print, here's what you'll need:
- The Google Chrome web browser.
- A regular or internet-enabled printer. (Virtually any printer is fine, but the setup process varies depending on the type of printer you have.)
- An active, internet-connected computer that the printer is connected to if it is not an internet-enabled printer.
- A Google account. (If you don't have one, sign up for one here.)
Once you've got all of that ready to go, you can start setting it up.
How to Set Up Google Cloud Print
There are two ways to set up your printers with Google Cloud Print. A handful of newer printers have internet connectivity built in and so you can connect them to Google directly. This process varies by printer, so (visit this page:http://www.google.com/cloudprint/learn/printers.html#setup-hp#setup-kodak#setup-epson ) to learn if your printer is compatible and, if so, how to set it up. If you have a traditional printer that's connected to your computer, however, the setup process is always the same. Just follow these steps: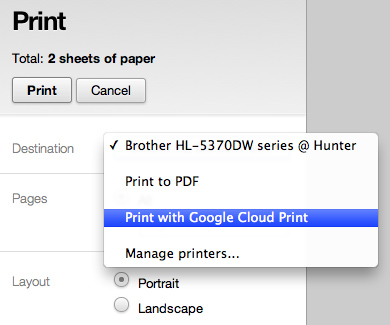
First, make sure everything is in place. You'll need Google Chrome installed on your computer. Also, ensure that your printer is connected to your computer, it's currently on, and you can print from it normally. (Note: You'll only be able to send print jobs to this printer when it is connected to your computer, so it's best to set this up on a desktop machine where the printer will always remain connected and powered on.)
- Once you have everything in place, open up Google Chrome and click the wrench icon in the upper right corner, choose "Options" ("Preferences" on a Mac), and then click the "Under the Hood" tab. Alternatively, just click this link. Now scroll down to the Google Cloud Print section towards the bottom and click "Sign in to Google Cloud Print."
- In the resulting window, sign in with your Google Account. This will enable the Cloud Print Connector on your computer.
- When a new message appears with a button labeled "Finish printer registration," click it.
- You'll receive a confirmation if everything worked properly, and it'll offer a link called "Manage your printers." Click on it to verify all the printers on your computer are now listed.
To test out your new setup, try printing something from within Google Chrome (such as this web page). When the printing options appear, choose "Print with Google Cloud Print" from the Destination menu. Click the "Print" button and you'll be asked to choose one of your cloud printers. Pick the one you want and, assuming everything is working correctly, your printer should print out a document.
Do More with Google Cloud Print
If you followed the instructions in the previous section, you already know how to print from a web page, but there's still more than you can do. Currently there are plenty of ways you can print from your smartphone, and even from your Mac desktop (if you prefer to avoid using Chrome for the task).
Print From Your Smartphone
Google Cloud Print has an tons of support in Android, of course, with a dedicated Android app and cloud printing support in the Google Docs Android app. You can also use third-party apps such as PrinterShare™ Mobile Print And Easy Print to get even more printing support out of Android. iOS users can check out PrintCentral Pro for iPhone and iPod touch or iPad to print with Google Cloud Print as well. Any mobile device can utilize cloud printing services by simply using Google's mobile web apps. Just visit m.google.com on your mobile device to get started.
Print from Your Mac
Strangely, there is no Windows app for Google Cloud Print but there is one for Mac OS X. It is aptly named Cloud Printer, and you can download it for free on the Mac App Store. It's not a perfect application, as it can only handle documents that Google Docs can view. Also, it doesn't function like an actual printer and instead requires you to choose a file you want to print from the dedicated app.





0 comments